| SYT5 |
|---|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | SYT5, synaptotagmin 5 |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 600782; MGI: 1926368; HomoloGene: 55722; GeneCards: SYT5; OMA:SYT5 - orthologs |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 19 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 19q13.42|11p | Start | 55,171,196 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 55,180,289 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 7 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 7|7 A1 | Start | 4,542,764 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 4,550,540 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - prefrontal cortex
- right frontal lobe
- cingulate gyrus
- anterior cingulate cortex
- nucleus accumbens
- caudate nucleus
- dorsolateral prefrontal cortex
- Brodmann area 9
- putamen
- Brodmann area 10
|
| | Top expressed in | - superior frontal gyrus
- primary visual cortex
- entorhinal cortex
- dentate gyrus of hippocampal formation granule cell
- perirhinal cortex
- CA3 field
- tongue
- anterior amygdaloid area
- ventromedial nucleus
- lateral septal nucleus
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 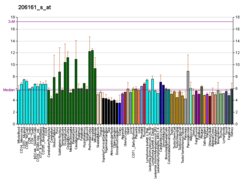
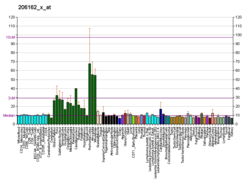 | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - clathrin binding
- metal ion binding
- protein heterodimerization activity
- calcium-dependent phospholipid binding
- syntaxin binding
- SNARE binding
- phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding
- phosphatidylserine binding
- calcium ion binding
| | Cellular component | - integral component of membrane
- endosome
- membrane
- synapse
- synaptic vesicle membrane
- cell junction
- neuronal cell body
- recycling endosome membrane
- perinuclear region of cytoplasm
- neuron projection
- dense core granule
- cytoplasmic vesicle
- plasma membrane
- proximal neuron projection
- integral component of neuronal dense core vesicle membrane
- axon
- exocytic vesicle
| | Biological process | - synaptic vesicle endocytosis
- chemical synaptic transmission
- vesicle fusion
- regulation of calcium ion-dependent exocytosis
- calcium ion-regulated exocytosis of neurotransmitter
- regulation of dopamine secretion
- synaptic vesicle exocytosis
- vesicle-mediated transport
- calcium-ion regulated exocytosis
- cellular response to calcium ion
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | | |
|---|
NM_016908
NM_001360421
NM_001360422 |
|
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | | |
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 19: 55.17 – 55.18 Mb | Chr 7: 4.54 – 4.55 Mb |
|---|
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|



















