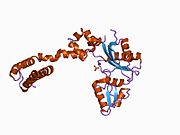
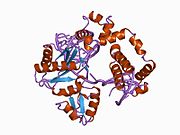
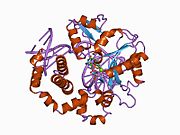
DNK polimeraza beta
| edit |
| DNK polimeraza beta | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
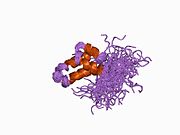
 PDB prikaz baziran na 1bno. | |||||||||||
| Dostupne strukture | |||||||||||
| 1BPX, 1BPY, 1BPZ, 1MQ2, 1MQ3, 1TV9, 1TVA, 1ZJM, 1ZJN, 1ZQA, 1ZQB, 1ZQC, 1ZQD, 1ZQE, 1ZQF, 1ZQG, 1ZQH, 1ZQI, 1ZQJ, 1ZQK, 1ZQL, 1ZQM, 1ZQN, 1ZQO, 1ZQP, 1ZQQ, 1ZQR, 1ZQS, 1ZQT, 2FMP, 2FMQ, 2FMS, 2I9G, 2ISO, 2ISP, 2P66, 2PXI, 3C2K, 3C2L, 3C2M, 3GDX, 3ISB, 3ISC, 3ISD, 3JPN, 3JPO, 3JPP, 3JPQ, 3JPR, 3JPS, 3JPT, 3LK9, 3MBY, 3OGU, 3RH4, 3RH5, 3RH6, 3RJE, 3RJF, 3RJG, 3RJH, 3RJI, 3RJJ, 3RJK, 3TFR, 3TFS, 7ICE, 7ICF, 7ICG, 7ICH, 7ICI, 7ICJ, 7ICK, 7ICL, 7ICM, 7ICN, 7ICO, 7ICP, 7ICQ, 7ICR, 7ICS, 7ICT, 7ICU, 7ICV, 8ICA, 8ICB, 8ICC, 8ICE, 8ICF, 8ICG, 8ICH, 8ICI, 8ICJ, 8ICK, 8ICL, 8ICM, 8ICN, 8ICO, 8ICP, 8ICQ, 8ICR, 8ICS, 8ICT, 8ICU, 8ICV, 8ICW, 8ICX, 8ICY, 8ICZ, 9ICA, 9ICB, 9ICC, 9ICE, 9ICF, 9ICG, 9ICH, 9ICI, 9ICJ, 9ICK, 9ICL, 9ICM, 9ICN, 9ICO, 9ICP, 9ICQ, 9ICR, 9ICS, 9ICT, 9ICU, 9ICV, 9ICW, 9ICX, 9ICY | |||||||||||
| Identifikatori | |||||||||||
| Simboli | POLB; MGC125976 | ||||||||||
| Vanjski ID | OMIM: 174760 MGI: 97740 HomoloGene: 2013 GeneCards: POLB Gene | ||||||||||
| EC broj | 2.7.7.7 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Pregled RNK izražavanja | |||||||||||
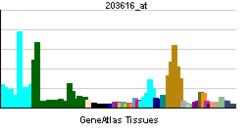 | |||||||||||
| podaci | |||||||||||
| Ortolozi | |||||||||||
| Vrsta | Čovek | Miš | |||||||||
| Entrez | 5423 | 18970 | |||||||||
| Ensembl | ENSG00000070501 | ENSMUSG00000031536 | |||||||||
| UniProt | P06746 | Q8K409 | |||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | NM_002690.2 | NM_011130.2 | |||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | NP_002681.1 | NP_035260.1 | |||||||||
| Lokacija (UCSC) | Chr 8: 42.2 - 42.23 Mb | Chr 8: 23.74 - 23.76 Mb | |||||||||
| PubMed pretraga | [1] | [2] | |||||||||
| Regulatorni element u POLB | |
|---|---|
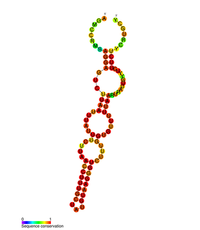 | |
| Predviđena sekundarna struktura stem loopII (M2) regulatornog elementa POLB | |
| Identifikatori | |
| Simbol | POLB |
| Rfam | RF01455 |
| Entrez | 5423 |
| HUGO | POLB |
| OMIM | 174760 |
| RefSeq | NM_002690 |
| Drugi podaci | |
| RNK tip | Cis-reg |
| Domain(i) | Mammalia |
| Lokus | Hromozom 8 p11.2 |
DNK polimeraza beta (POLB) je enzim koji kod ljudi kodira POLB gen.[1]
Funkcija
U eukariotskim ćelijama, DNK polimeraza beta (POLB) izvodi popravke ekscizijom baza (BER) koje su neophodne za popravku DNK, replikaciju, rekombinaciju, i otpornost na lekove.[1]
Regulacija ekspresije
DNK polimeraza beta održava genomski integritet putem uzimanja učešća u popravci ekscizijom baza. Prekomerno izražavanje POLB iRNK je u korelaciji sa brojnim tipovima kancera, dok deficijencije POLB-a rezultuju u hipersenzitivnosti na alkilirajuće agense, uključujući apoptozu, i prekid hromozoma.[2] Iz tih razloga, esencijalno je precizno održavanje kontrole POLB ekspresije.[3][4][5][6]
Interakcije
DNA polimeraza beta formira interakcije sa PNKP[7] i XRCC1.[8][9][10][11]
Reference
- ↑ 1,0 1,1 „Entrez Gene: POLB polymerase (DNA directed), beta”.
- ↑ Narayan S, He F, Wilson SH (August 1996). „Activation of the human DNA polymerase beta promoter by a DNA-alkylating agent through induced phosphorylation of cAMP response element-binding protein-1”. J. Biol. Chem. 271 (31): 18508–13. DOI:10.1074/jbc.271.31.18508. PMID 8702497.
- ↑ Canitrot Y, Cazaux C, Fréchet M i dr.. (October 1998). „Overexpression of DNA polymerase beta in cell results in a mutator phenotype and a decreased sensitivity to anticancer drugs”. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 95 (21): 12586–90. DOI:10.1073/pnas.95.21.12586. PMC 22874. PMID 9770529.
- ↑ Bergoglio V, Pillaire MJ, Lacroix-Triki M i dr.. (June 2002). „Deregulated DNA polymerase beta induces chromosome instability and tumorigenesis”. Cancer Res. 62 (12): 3511–4. PMID 12067997.
- ↑ Bergoglio V, Canitrot Y, Hogarth L i dr.. (September 2001). „Enhanced expression and activity of DNA polymerase beta in human ovarian tumor cells: impact on sensitivity towards antitumor agents”. Oncogene 20 (43): 6181–7. DOI:10.1038/sj.onc.1204743. PMID 11593426.
- ↑ Srivastava DK, Husain I, Arteaga CL, Wilson SH (June 1999). „DNA polymerase beta expression differences in selected human tumors and cell lines”. Carcinogenesis 20 (6): 1049–54. DOI:10.1093/carcin/20.6.1049. PMID 10357787.
- ↑ Whitehouse, C J; Taylor R M, Thistlethwaite A, Zhang H, Karimi-Busheri F, Lasko D D, Weinfeld M, Caldecott K W (January 2001). „XRCC1 stimulates human polynucleotide kinase activity at damaged DNA termini and accelerates DNA single-strand break repair”. Cell (United States) 104 (1): 107–17. DOI:10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00195-7. ISSN 0092-8674. PMID 11163244.
- ↑ Wang, Liming; Bhattacharyya Nandan, Chelsea Diane M, Escobar Pedro F, Banerjee Sipra (November 2004). „A novel nuclear protein, MGC5306 interacts with DNA polymerase beta and has a potential role in cellular phenotype”. Cancer Res. (United States) 64 (21): 7673–7. DOI:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-2801. ISSN 0008-5472. PMID 15520167.
- ↑ Fan, Jinshui; Otterlei Marit, Wong Heng-Kuan, Tomkinson Alan E, Wilson David M (2004). „XRCC1 co-localizes and physically interacts with PCNA”. Nucleic Acids Res. (England) 32 (7): 2193–201. DOI:10.1093/nar/gkh556. PMC 407833. PMID 15107487.
- ↑ Kubota, Y; Nash R A, Klungland A, Schär P, Barnes D E, Lindahl T (December 1996). „Reconstitution of DNA base excision-repair with purified human proteins: interaction between DNA polymerase beta and the XRCC1 protein”. EMBO J. (ENGLAND) 15 (23): 6662–70. ISSN 0261-4189. PMC 452490. PMID 8978692.
- ↑ Bhattacharyya, N; Banerjee S (July 2001). „A novel role of XRCC1 in the functions of a DNA polymerase beta variant”. Biochemistry (United States) 40 (30): 9005–13. DOI:10.1021/bi0028789. ISSN 0006-2960. PMID 11467963.
Literatura
- Date T, Tanihara K, Yamamoto S i dr.. (1992). „Two regions in human DNA polymerase beta mRNA suppress translation in Escherichia coli”. Nucleic Acids Res. 20 (18): 4859–64. DOI:10.1093/nar/20.18.4859. PMC 334243. PMID 1408801.
- Wang L, Patel U, Ghosh L, Banerjee S (1992). „DNA polymerase beta mutations in human colorectal cancer”. Cancer Res. 52 (17): 4824–7. PMID 1511447.
- Tokui T, Inagaki M, Nishizawa K i dr.. (1991). „Inactivation of DNA polymerase beta by in vitro phosphorylation with protein kinase C”. J. Biol. Chem. 266 (17): 10820–4. PMID 2040602.
- SenGupta DN, Zmudzka BZ, Kumar P i dr.. (1986). „Sequence of human DNA polymerase beta mRNA obtained through cDNA cloning”. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 136 (1): 341–7. DOI:10.1016/0006-291X(86)90916-2. PMID 2423078.
- Zmudzka BZ, Fornace A, Collins J, Wilson SH (1988). „Characterization of DNA polymerase beta mRNA: cell-cycle and growth response in cultured human cells”. Nucleic Acids Res. 16 (20): 9587–96. DOI:10.1093/nar/16.20.9587. PMC 338765. PMID 2460824.
- Widen SG, Kedar P, Wilson SH (1988). „Human beta-polymerase gene. Structure of the 5'-flanking region and active promoter”. J. Biol. Chem. 263 (32): 16992–8. PMID 3182828.
- Abbotts J, SenGupta DN, Zmudzka B i dr.. (1988). „Expression of human DNA polymerase beta in Escherichia coli and characterization of the recombinant enzyme”. Biochemistry 27 (3): 901–9. DOI:10.1021/bi00403a010. PMID 3284575.
- Dobashi Y, Kubota Y, Shuin T i dr.. (1995). „Polymorphisms in the human DNA polymerase beta gene”. Hum. Genet. 95 (4): 389–90. PMID 7705833.
- Chyan YJ, Ackerman S, Shepherd NS i dr.. (1994). „The human DNA polymerase beta gene structure. Evidence of alternative splicing in gene expression”. Nucleic Acids Res. 22 (14): 2719–25. DOI:10.1093/nar/22.14.2719. PMC 308239. PMID 7914364.
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (1994). „Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides”. Gene 138 (1–2): 171–4. DOI:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
- Chang M, Burmer GC, Sweasy J i dr.. (1994). „Evidence against DNA polymerase beta as a candidate gene for Werner syndrome”. Hum. Genet. 93 (5): 507–12. PMID 8168825.
- Chyan YJ, Strauss PR, Wood TG, Wilson SH (1996). „Identification of novel mRNA isoforms for human DNA polymerase beta”. DNA Cell Biol. 15 (8): 653–9. DOI:10.1089/dna.1996.15.653. PMID 8769567.
- Pelletier H, Sawaya MR, Wolfle W i dr.. (1996). „Crystal structures of human DNA polymerase beta complexed with DNA: implications for catalytic mechanism, processivity, and fidelity”. Biochemistry 35 (39): 12742–61. DOI:10.1021/bi952955d. PMID 8841118.
- Pelletier H, Sawaya MR, Wolfle W i dr.. (1996). „A structural basis for metal ion mutagenicity and nucleotide selectivity in human DNA polymerase beta”. Biochemistry 35 (39): 12762–77. DOI:10.1021/bi9529566. PMID 8841119.
- Pelletier H, Sawaya MR (1996). „Characterization of the metal ion binding helix-hairpin-helix motifs in human DNA polymerase beta by X-ray structural analysis”. Biochemistry 35 (39): 12778–87. DOI:10.1021/bi960790i. PMID 8841120.
- Kubota Y, Nash RA, Klungland A i dr.. (1997). „Reconstitution of DNA base excision-repair with purified human proteins: interaction between DNA polymerase beta and the XRCC1 protein”. EMBO J. 15 (23): 6662–70. PMC 452490. PMID 8978692.
- Bennett RA, Wilson DM, Wong D, Demple B (1997). „Interaction of human apurinic endonuclease and DNA polymerase beta in the base excision repair pathway”. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 94 (14): 7166–9. DOI:10.1073/pnas.94.14.7166. PMC 23779. PMID 9207062.
- Sawaya MR, Prasad R, Wilson SH i dr.. (1997). „Crystal structures of human DNA polymerase beta complexed with gapped and nicked DNA: evidence for an induced fit mechanism”. Biochemistry 36 (37): 11205–15. DOI:10.1021/bi9703812. PMID 9287163.
- Bhattacharyya N, Banerjee S (1997). „A variant of DNA polymerase beta acts as a dominant negative mutant”. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 94 (19): 10324–9. DOI:10.1073/pnas.94.19.10324. PMC 23361. PMID 9294209.
- Suzuki Y, Yoshitomo-Nakagawa K, Maruyama K i dr.. (1997). „Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5'-end-enriched cDNA library”. Gene 200 (1–2): 149–56. DOI:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3. PMID 9373149.
Vidi još
- POLA1
- POLA2
Spoljašnje veze
- Rfam entry for the stem loopII (M2) regulatory element in POLB[mrtav link]
- p
- r
- u
|